In our last Clery post, entitled “ASUPD misrepresents its crime statistics, violates Clery Act (Part One)” , we looked at what the Clery Act is, what reporting is required of universities who are obligated to adhere to Clery, and why the Clery Act is so important. In this second installment, we are going to discuss how exactly ASUPD is misrepresenting its crime statistics (and how that violates the requirements of the Clery Act).
1. ASUPD omits crime stats from specific reporting areas required under the Clery Act
In our previous post about the Clery act, we discussed different areas other than campus ASU is required to provide crime statistics for, namely:
Public Property
- Public property (All public property, including thoroughfares, streets, sidewalks, and parking facilities, that is within the campus, or immediately adjacent to and accessible from the campus, as well as any public transit stops adjacent to campus).
However, according to page 33 of ASU’s 2013 Annual Security and Crime Safety report, we found this small disclaimer:

Similarly, on page 34 of the Crime Safety report, we found this disclaimer for West, Poly, Downtown and Lake Havasu campus’ public property reporting:

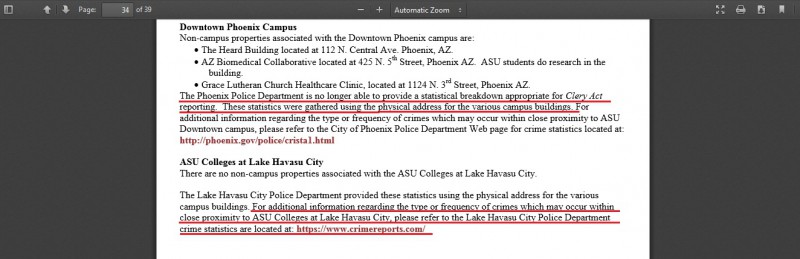
So essentially, what ASUPD is telling the public via the Crime safety report is that the crime stats on the report do NOT include areas adjacent to ANY campus, nor do they include the crime stats for the EIGHTEEN areas considered “non campus properties”.
ASUPD’s excuse for not including public property crimes is that ASU “is unable to provide a statistical breakdown appropriate for Clery Act reporting” is a weak excuse. The “Handbook for Campus Safety and Security Reporting” requires a university to show a “good faith” effort to collect crime data from another non-university police agency.
This “disclaimer” about not having statistical data appropriate for Clery reporting is to be utilized when other agencies refuse to release their crime statistics, or the information provided to the university is unable to be attributed to ANY of the university’s Clery geography (page 103). ASU IS provided crime stats/information (by Tempe PD) that are able to be broken down to the “public property” level simply by looking at the physical location of the offense; this is the type of work that crime analysts routinely engage in.
ASU is also able to request the crime stats for their non-campus properities by merely providing the address of the property to the appropriate jurisdiction. We reached out to Scottsdale PD, home of Skysong (one of the non-campus property locations) and we were told that ASU contacted them approximately one time to request crime information.
We accessed the database referenced in page 33 of the Crime Safety report to see what crimes ASU may have missed because of its exclusion of public property statistics, and this is what we found for ASU’s Tempe Campus:
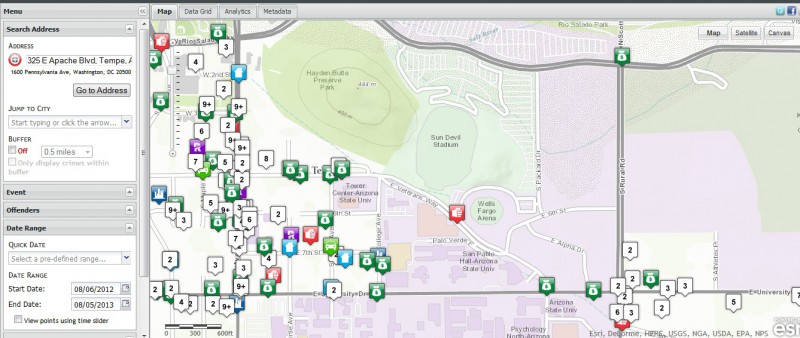
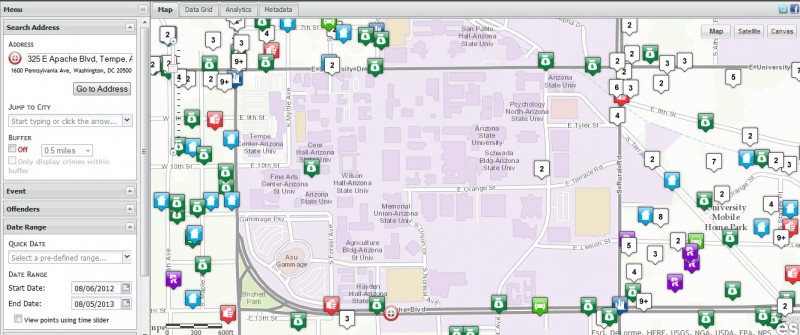
ASU excluded a significant amount of crimes occurring adjacent to campus (and several that occurred ON campus but were handled by other police agencies) from its Crime Safety Report (go to raidsonline.com and use the date range of August 2012-August 2013 to view the above posted data in a clickable format)
Non-campus property
- Non-campus property: Owned or controlled by a student organization that is officially recognized; any building or property owned or controlled by an institution that is used in direct support of, or in relation to, the institution’s educational purposes; not within the same reasonably contiguous geographic area of the institution.
These are the non-campus statistics from ASU’s Skysong Campus which are not included on the Tempe non-campus property in the Crime Safety report (cited from raidsonline.com, using the date range of August 2012-August 2013): Note that the campus boundary is marked with a solid blue line, and each of the crimes are circled in red.
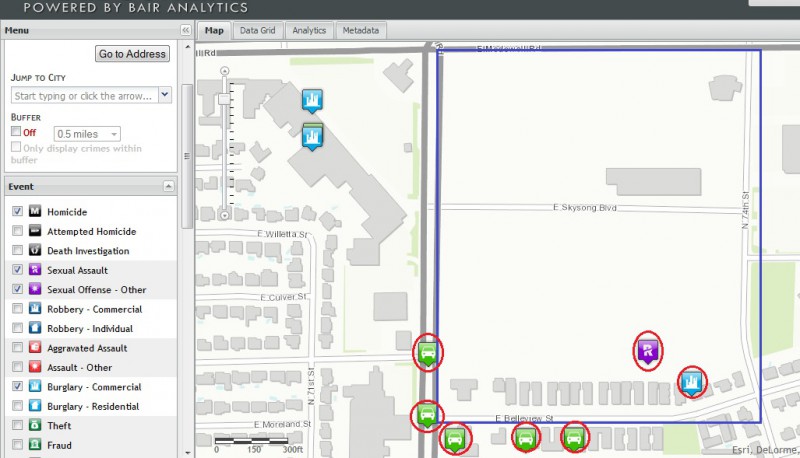
Note there are five motor vehicle thefts, one sexual assault, and one commercial burglary NOT included in ASU’s Crime Safety Report.
2. ASUPD improperly classifies crimes so they don’t meet the criteria for Clery reporting
Sex offenses
Perhaps the most misclassified/reclassified type of crime are those linked to sex offenses. Clery Act has a much more broad definition of what a sex offense is compared to definition used by the UCR (which excludes forcible fondling). Under the Clery Act, there are two types of sex offenses: forcible and non-forcible.
- Forcible sex offense: Forcible rape, forcible sodomy, sexual assault with an object, forcible fondling.
- Non-forcible sex offense: Incest, statutory rape.
“Schools can wrongly categorize reports of acquaintance rape or fondling as “non-forcible” sexual offenses — a definition that should only apply to incest and statutory rape”, according to an article by publicintegrity.org.
In August 2007, an ASU student reported being sexually assaulted at the Sigma Chi fraternity house. Subsequent follow-up emails to then Assistant Chief Jay Spradling went unanswered, and the sexual assault was later reclassified. The student alleged that her sexual assault was not investigated by Officer Janda (who documented the assault on a field investigation card) because she was intoxicated. Clery specifically states that a sex offense is presumed to be forcible if the person is incapable of giving consent “due to his or temporary/permanent physical or mental incapacity”.
The woman, who later sued the Arizona Board of Regents for violating Title IX, stated ASU has in recent years systematically and severely underreported sexual assault reports. Her complaint states that in 2008, ASU reported and posted only four forcible sexual assault reports in its 2009 Annual Security Reports, despite, on information and belief, having received at least several dozen reports.
A 2010 State Press article interviewed a counselor who works with sexual assault victims and is closely affiliated with the university and stated, “ASU does not take sexual assault reports seriously enough, creating a climate that keeps victims quiet and crime stats low”.
In 2011, ASUPD arrested a man accused of fondling at least 14 victims on ASU’s campus the previous year. Under the Clery reporting guidelines, forcible fondling is required to be reported as a forcible sex offense. For the year the incidents occurred (2010), ASU reported a mere 6 forcible sex offenses that occurred on campus (see Campus_Security_Policy )
Prevalence of under reporting sexual assaults
USC, UC Berkley, and Occidental College are all major universities currently facing the possibility of sanctions from the Department of Education for failing to properly report the number of sexual assaults on campus.
Robbery
ASU has also reclassified several robberies into felony thefts, which would prevent their inclusion into ASU’s Crime Safety Report. Under the Clery Act, robbery is defined as:
ASU has had several strong arm robbery series which occurred on ASU’s campus where the victim was robbed of an IPhone and then dragged by a vehicle; under the Clery Act, these crimes should have been listed as a “robbery”, but they were later reclassified to a “felony theft” or merely “theft”.
3. ASU doesn’t utilize its resources properly
While formal training in the field of statistics and crime analysis is not required for persons preparing the Crime Safety Report under the guidelines specified by the Clery Act, that type of knowledge is useful when tasked with processing a large amount of data in a relatively short period of time. ASUPD has been fortunate to have a crime analyst on board for the past few years, but unfortunately, the analysts’ job has been reduced to producing crime maps for bike thefts on campus.
ASU’s former analyst (who has subsequently left the department for greener pastures) was much more qualified to process and analyze crime data compared to the Commander in charge of Clery reporting (Michele Rourke), who merely possesses a bachelor’s degree in English and has no formal training in statistics
Additionally, with such a large criminal justice undergraduate/graduate program, ASUPD could utilize several unpaid student volunteers or interns to process and catalog crime reports; this is a relatively common practice in larger departments such as Tempe PD.
4. ASU needs stronger partnerships with other agencies
After looking at the various locations where ASU has property/research labs, it is obvious that the university’s footprint is pretty significant. ASU has demonstrated that it does not have the resources, training, or personnel to effectively fulfill its obligations under the Clery Act; ASU needs to form stronger partnerships and more effective ways to communicate with other police departments. Building a rapport with another agency would assist ASU in obtaining the proper crime information necessary for a thorough Crime Safety report, and perhaps allowing ASU to assist that agency in some other area in the future.
All of this information, especially when coupled with the storm of negative media coverage over ASU’s crime situation, are evidence that ASU’s students/faculty/staff are NOT as safe as the university would lead them to believe. ASUPD knows the magnitude of the crime problems on and around all campuses, but refuses to do anything about it.
There is no more hiding behind Tempe PD or any other police agencies; the other agencies did not create the staffing shortages, the lack of training, or incentives to stay in the department—you did, Command staff! ASUPD is unable to fulfill its basic obligation to serve and protect its community. It is now a matter of time before ASU starts losing students (and $$) because of these shocking safety issues.






